Right Triangle Trigonometry part 2
Instructor Katherine Cliff
Warm up: Simplify the following expression if possible.
\[\frac{3+6x}{x+2x^2}\]
A. \(3x\)
B. Not possible
C. \(\frac{3}{x}\)
D. \(\frac{3+3x}{x+2x^2}\)
Announcements/reminders
Grades and feedback in myopenmath
Exam 1 in two weeks!
Example: Calculate sin(α), cos(α), and tan(α) given the following triangle:
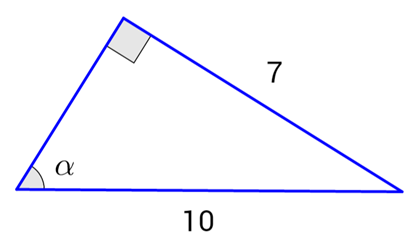
Work on number 1 in your packet.
Consider the equilateral triangle pictured below:
When we draw an altitude connecting the top corner to the base of the triangle, we’ve created our first special right triangle, a \(30^\circ-60^\circ-90^\circ\) triangle. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for the height of the triangle, then use this triangle to find the sine and cosine of \(30^\circ\) and the sine and cosine of \(60^\circ\).
Consider the equilateral triangle pictured below:
Special Right Triangle
Use what you’ve learned to find the sines and cosines of \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) and \(\frac{\pi}{3}\).
Now work on numbers 3 and 4 in the packet.
We’ve created our second special right triangle, a \(45^\circ-45^\circ-90^\circ\) triangle. Use it to find the sine and cosine of \(45^\circ\).
Now use what you’ve learned to find the sine and cosine of \(\frac{\pi}{4}\).
Reciprocal Trigonometric Ratios
Important note about the reciprocal ratios!!!!
Example:
Calculate csc(α), sec(α), and cot(α) given the following triangle:
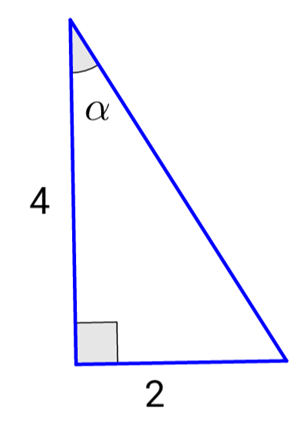
Example:
Calculate csc(α), sec(α), and cot(α) given the following triangle:

Using Right Triangle Trig to solve for missing information.
What do we do if we don’t have a special triangle?
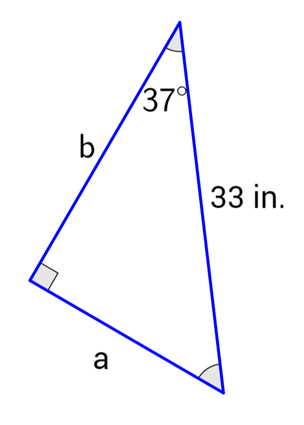
Example: Find the value of a 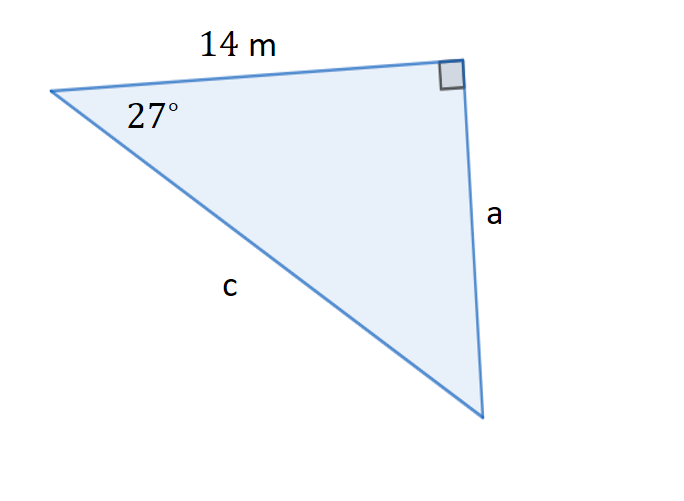
Example: Find the value of a
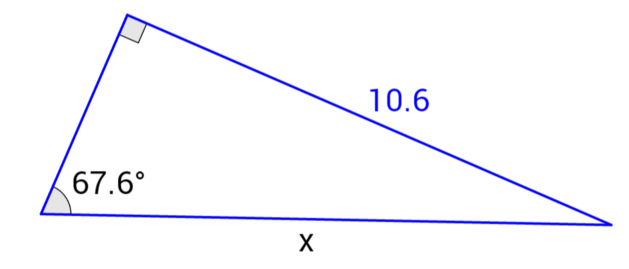
Example: Find the value of x
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
In a right triangle with reference angle \(\theta\)…
If \(\sin(\theta) = n\), then \(\sin^{-1}(n) = \theta\) or \(\arcsin(n)=\theta\).
If \(\cos(\theta) = n\), then \(\cos^{-1}(n) = \theta\) or \(\arccos(n)=\theta\).
If \(\tan(\theta) = n\), then \(\tan^{-1}(n) = \theta\) or \(\arctan(n)=\theta\).
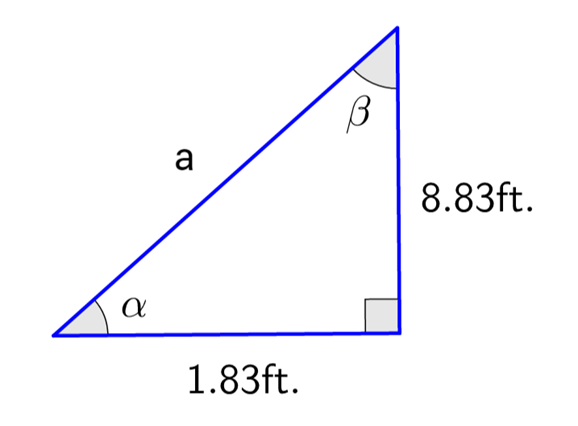
Example: Solve for \(\alpha\)
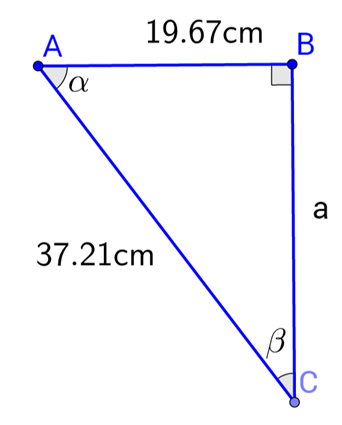
Example: Solve for \(\beta\)
A. \(\arccos\left(\frac{19.67}{37.21}\right)\)
B. \(\arcsin\left(\frac{19.67}{37.21}\right)\)
C. \(\frac{1}{\sin\left(\frac{19.67}{37.21}\right)}\)
D. \(\frac{1}{\cos\left(\frac{19.67}{37.21}\right)}\)
Example: Solve for \(\alpha\)